How to improve sales forecast accuracy is a million-dollar question for businesses looking to predict future revenue. And if you’re here, you likely want to know the answer to that question too.
While perfect predictions may not be possible, increased accuracy is within reach. The key is blending quantitative data with qualitative insights to get a complete picture. Aim for reasonable precision, not perfection.
Of course, accurate forecasting is easier said than done. But by using these forecasting best practices, you can boost the accuracy of your next forecast and set your sales team up for success.
Topics covered:
- Forecast accuracy definition
- What is a good forecast accuracy percentage?
- Tips to improve the accuracy of your sales forecasts
What is the definition of forecast accuracy?
Forecast accuracy refers to the degree to which a predicted value matches up with the actual result. Simply put, it's how close you can get your sales predictions to what ultimately happens.
Higher forecast accuracy means your predictions consistently and reliably reflect the direction of future performance. Perfection is unrealistic - there are always uncertainties. But with a sound forecasting process, you can achieve solid accuracy quarter after quarter.
What is a good forecast accuracy percentage?
A good sales forecast accuracy depends on the industry, the volatility of the market, and the forecasting method used. However, most industries consider a sales forecast accuracy within 10% of your forecast as pretty good.
For example, if a company predicted they would sell 100 units of a product and they sold 95, their forecast accuracy would be 95%. This is a commendable rate.
Forecast accuracy formula:
Day 1 Forecast – Actual Sales) / Actual Sales * 100%
However, achieving such a high rate of accuracy isn’t always feasible. Intangent reports that 80% of sales organizations don’t have a forecast accuracy greater than 75%. And 93% of sales leaders are unable to forecast revenue within 5%, even with two weeks left in the quarter.
But that’s not all. Here are some more interesting (albeit shocking) statistics to note:
- Less than 50% of sales leaders and sellers have high confidence in their company's forecasting accuracy. (Gartner’s ‘State of Sales Operations Survey’)
- 55% of sales leaders do not have high confidence in their forecasting accuracy. (Intangent)
- 67% of organizations lack a formalized approach to forecasting altogether. (Intangent)
- The top 24% of sales teams are 1.5 times more likely to base forecasts on data-driven insights. (Salesforce)
The data paints a clear picture - there is significant room for improving sales forecast accuracy across most organizations. While perfection is not attainable, striving for a high degree of precision is possible with the right approach.
By leveraging data, insights, and robust processes, top-performing teams can boost accuracy and operate with greater visibility.

How to improve sales forecast accuracy
Now let's dive into proven tactics to improve forecast accuracy. Applying the following strategies will help you to develop predictions that inspire confidence and drive better decisions.
So, here are our top tips on how to improve sales forecasting accuracy:
1. Create a simple model
If you don’t know where to start, keep it simple. This is an effective approach because a basic model is an adaptable model. With it, you can grasp the foundational elements of sales trends without getting stuck in complexity.
With fewer variables, it’s easier to communicate the reasoning behind your forecast and obtain approval from leadership. For example, starting with a regression forecasting model for several sales activities will be a lot more manageable than throwing in all types of variables and trying to make it work.
Of course, that’s not to say that a more complex forecast wouldn’t work. But if you want to test a new model, starting simple ensures the sales forecast remains responsive to changing business realities, without the risk of overcomplicating the process from the outset.
As the company gathers more data and learns more about its sales patterns, it can improve the model.
2. Keep clean records and validate data sources
You’ve probably heard the saying, garbage in, garbage out. Any errors, duplications, or outdated data will be incorporated into forecast models, reducing reliability.
Clean data = accurate data.
Clean records and validated data sources are critical for increasing sales forecast accuracy for a few key reasons:
- With clean sales data, it’s easier to spot trends, cycles, and trajectories that inform future projections.
- Data inputs need to originate from credible, consistent sources. Unvalidated market research or biased rep forecasts distort models.
- Quality data and vetted sources consolidate the bedrock that precise forecasts are built on, forming the foundation for accuracy. Flawed data undermines accuracy.
The integrity of your sales forecast is significantly influenced by the credibility of the data. So, you must be diligent in making sure the data used in your forecasting process is validated, originated from trusted sources, and updated consistently.

3. Use historical data
When creating sales forecasts based on historical data, past performance provides invaluable context. By analyzing previous sales trends, you expose seasonal fluctuations, growth trajectories, and the impact of past strategies. This enables pattern recognition that informs future projections.
Evaluating how to forecast sales based on historical data allows you to spot where cycles exist. Which months see spikes or dips? How has growth progressed year over year? What catalysts previously drove major gains or declines? The answers shape reliable assumptions.
With this hindsight, you can set realistic targets and account for seasonal variations. Past trends become reference points to calibrate your models.
Isolate factors that disrupted past forecasts and adjust your lens. Historical data anchors your forecast in realism while revealing opportunities for improvement.
4. Use the right sales forecasting method
Choosing the right forecasting approach is crucial for improving forecast accuracy. Different methods have strengths and weaknesses based on your business model, sales cycle, and data availability.
Align the methodology with your unique needs and processes. Shorter-term tactical forecasts may leverage different techniques than long-range strategic projections.
Consider options like:
Top-down vs bottom-up forecasting
The top-down method starts with high-level estimates and breaks them down into smaller targets; it's effective with clear strategy and established sales patterns.
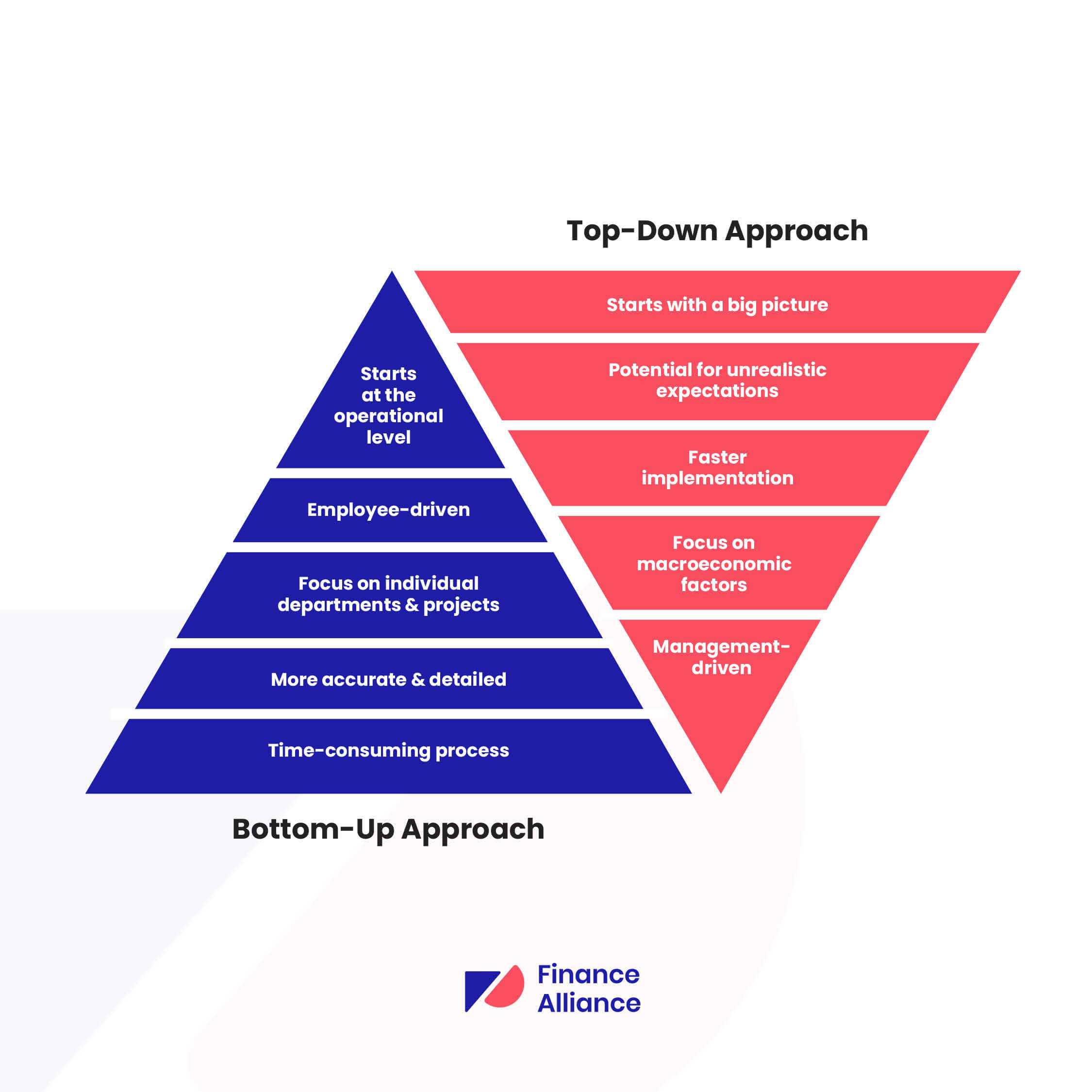
Bottom-up starts with local projections and aggregates them, excelling when diverse products or large deals are involved. Evaluate your sales landscape to choose the best method for clear forecasting.
A blended approach is also an option.
Pipeline forecasting
This method focuses on current deals or leads in the sales process. It evaluates the likelihood of each deal closing based on its stage in the sales pipeline.
For example, a lead in the final negotiation phase might have a higher chance of converting than one in the initial contact phase. By weighing these probabilities, companies can predict their future sales.
Historical trend analysis
As we previously mentioned, historical forecasting looks at past sales patterns and seasonality to estimate future trends.
Some pros and cons to consider:
Pros:
- Easy peasy: One of the best things about historical forecasting is its simplicity. Got past sales data? Plug it in, and you’re well on your way to creating an in-depth forecast based on your own data.
- The devil you know: When your sales have had a steady rhythm, historical data can be incredibly useful. You can use it to compare month-over-month or year-over-year revenue with fairly accurate results.
- Budget-friendly: No need to hire a team of analysts or invest in fancy software. A solid Excel sheet or basic CRM could give you enough juice to make decent projections.
Cons:
- Past ≠ future: If your market’s changing faster than a chameleon on a rainbow, historical data can be misleading.
- Blind spots: New competitors entering the ring? A potential economic downturn? Historical forecasting won't warn you. It’s like trying to drive using only the rearview mirror.
- Missed opportunities: Relying too much on the past could mean you’re not agile enough to capitalize on new trends or markets. While you're looking back, your more adaptive competitors could zoom past you.
Some other methods (and sales forecasts strategies) include:
- Regression forecasting: This method uses statistical algorithms to identify the relationships between sales and one or more influencing factors like advertising spend or market trends. It's super useful for understanding how various elements could impact your sales trajectory.
- Opportunity stage forecasting: Here, you estimate the likelihood of a sale based on the current stage of each opportunity in your sales pipeline. It's great for giving a nuanced view of short-term revenues.
- Opportunity creation forecasting: This focuses on the rate at which new sales opportunities or leads are being created. It helps you understand if you're generating enough new business to meet future sales goals.
- Length of sales cycle forecasting: By analyzing how long it typically takes to close a deal, you can predict when current opportunities will likely turn into revenue. It's good for long-term planning and resource allocation.
- Seasonal forecasting: This method considers seasonal trends and cycles in the industry, helping you plan inventory and staffing around high- and low-sales periods.
- Lead-driven forecasting: This starts with the number and quality of leads in your sales funnel to predict sales. It's fantastic for scaling efforts—knowing what each lead can potentially bring in helps you allocate resources wisely.
- Multi-variable analysis forecasting: This one's the Swiss Army knife of forecasting. It combines various factors like market conditions, seasonality, and lead quality to provide a comprehensive view of future sales.
- Test-market analysis forecasting: By introducing a product to a limited market, you can gauge its future success. It's a proactive way to validate if a new launch will soar or sink before going all in.
- Intuitive forecasting: This relies on the experience and gut feelings of your sales team. It may not be data-driven, but it can capture intangibles like market sentiment.
- Time series forecasting: This method uses past sales data to identify trends or patterns over time, helping you make educated guesses on future sales. It's the go-to for businesses with stable, repetitive sales cycles.
- Demand forecasting: This aims to predict consumer demand for your products or services. It’s crucial for inventory management, helping you stock up just right—neither too much nor too little.
Choose an approach that aligns with your sales cycle, available data, and resources. Blend methods to optimize strengths and minimize blind spots.

5. Integrate influencing factors
If you've given all the above methods a whirl and you're still not hitting the mark, it might be time to dig deeper with some qualitative insights. There could be other hidden variables, either inside or outside your organization, that your existing sales forecast process is missing.
If you want to know how to improve forecasting accuracy, take a look at some likely elements that could be throwing off your predictions:
Seasonality
Let's start with the weather—well, sort of. We're talking about the 'climate' of your sales. If you have a forecast accuracy dashboard, pay attention to seasonal spikes or dips. Many businesses experience fluctuations in sales due to various seasonal factors, whether it's retail sales spiking during the holiday season or a drop in tourism-related sales during off-peak months. Knowing when your products are hot (or not) is key to improving sales forecast accuracy.
Market changes
Are you keeping tabs on your market? If a new competitor struts into town or a popular product starts trending, you'll want to know ASAP. This can either be a hurdle or an opportunity. Either way, plug these changes into your forecasts to stay ahead of the curve.
Economic conditions
No sales forecast lives in a vacuum. It's influenced by everything from inflation rates to unemployment numbers. So, if you're scratching your head about how to improve sales forecast accuracy, consider economic indicators. A cautious peek into economic reports can give you a more nuanced view of what to expect.
Business changes
Is your company rolling the red carpet out for new hires? Or perhaps you're launching a new product or tweaking pricing? These internal shake-ups need to be accounted for in your sales forecast. Updates like these can send ripples across your forecast accuracy dashboard. Ignoring them is like ignoring a leaky faucet—annoying at first, disastrous over time.
Legislative changes
New taxes, trade tariffs, or compliance regulations can play a big role in your sales numbers. When legislation changes, the first place you'll see the impact is on your bottom line. So, you'd do well to factor these shifts into your strategy on how to improve sales forecast accuracy.
6. Leverage modern technology for precision
If you're still juggling spreadsheets or scratching your head over an abacus, it's time to step into the 21st century. Leveraging technology isn't just trendy - it's practically a must-do for anyone serious about sharpening their sales forecast accuracy.
Here are a few ways you can leverage technology to help improve forecast accuracy:
AI and Machine Learning
Imagine having a mini-Einstein in your computer, crunching numbers while you sip your latte. That's AI for you.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can sift through mountains of data very quickly. They not only look at historical trends but can also consider a plethora of variables you might not even be aware of.
Plus, as AI systems are trained over time, their predictions become increasingly precise.

CRM systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have come a long way and can now integrate with your sales data and even offer built-in forecasting tools.
A CRM keeps all your info in one place and makes it much simpler to track changes that could impact sales, such as a high-performing sales rep leaving or a new product launching.
Automate data collection
Automated data collection tools can sync up with various data sources and funnel them right into your forecasting model. They save time, reduce errors, and most importantly, allow you to focus on what really matters: strategic planning.
Use forecasting tools
The digital age presents a plethora of advanced sales forecasting software and tools, tailored to streamline and enhance the prediction process. By tapping into these technologies, you can automatically analyze vast datasets, spot patterns more efficiently, and adjust predictions in real time.
Consistently review technology
While technology does the heavy lifting, human oversight remains crucial. Setting up regular review intervals using these technological tools ensures that the forecast remains in line with real-world developments.
Regularly updating and refining predictions with the aid of technology ensures forecasts are both current and relevant.

7. Prioritize cross-department collaboration
For a sales forecast to truly resonate with accuracy, it must be informed by a holistic view of the organization. This means incorporating insights not just from the sales team, but also from marketing, operations, and customer service.
Every team brings its own flair to the table, spotting trends or red flags that others might miss. By setting up inter-departmental meetings, finance teams can refine forecasts by incorporating a wide array of valuable insights, ensuring the predictions are both comprehensive and precise.
Sales team input
The frontline sales team is often the first to witness shifts in market demands or customer preferences. Their on-the-ground experiences are invaluable for accurate forecasting.
Encouraging regular feedback and insights from them ensures that the forecast is rooted in real-world observations.
You should also consider training the sales team on the importance of accurate data input to ensure information fed into forecasting models is both reliable and relevant, reducing the chance of skewed predictions.
FAQs: Sales forecast accuracy
What factors affect a sales forecast?
Several factors can affect a sales forecast, including market conditions, economic indicators, seasonality, competitor activities, and internal changes like new hires or product launches. External legislative changes can also impact forecasts. Understanding these variables and how they interact is crucial for creating a reliable sales forecast.
What things can make sales forecasts inaccurate?
Inaccurate data, outdated methods, lack of cross-departmental input, and failing to adapt to market changes can all make a sales forecast inaccurate. Overreliance on gut instinct or overly optimistic projections can also skew results, leading to poor decision-making and missed opportunities.
What is the key to successful forecasting?
The key to successful forecasting lies in integrating accurate data, utilizing advanced analytical methods, and maintaining an agile approach that allows for quick adaptation to changing conditions. Continuously updating and improving your forecasting model ensures that it remains a useful tool for strategic planning.
Why improve forecast accuracy?
Improving forecast accuracy is crucial for strategic planning, risk management, and resource allocation. Accurate forecasts allow businesses to make informed decisions, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate potential risks, thereby enhancing overall organizational performance.
What is forecast accuracy based on?
Forecast accuracy is based on how closely predicted numbers align with actual outcomes. It is typically measured by comparing the forecasted figures to the actual sales for a given period, often using metrics like Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) or Forecast Error. High forecast accuracy indicates a reliable, well-calibrated model and effective planning.





